Importance of Line Numbering in the Piping Design Process
Line numbering is a fundamental, yet often underappreciated, element within the complex discipline of piping design. Far from being a mere administrative detail, a systematic and robust line numbering scheme is crucial for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and operational integrity of industrial facilities, particularly in sectors like oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation.
The Role of Line Numbering
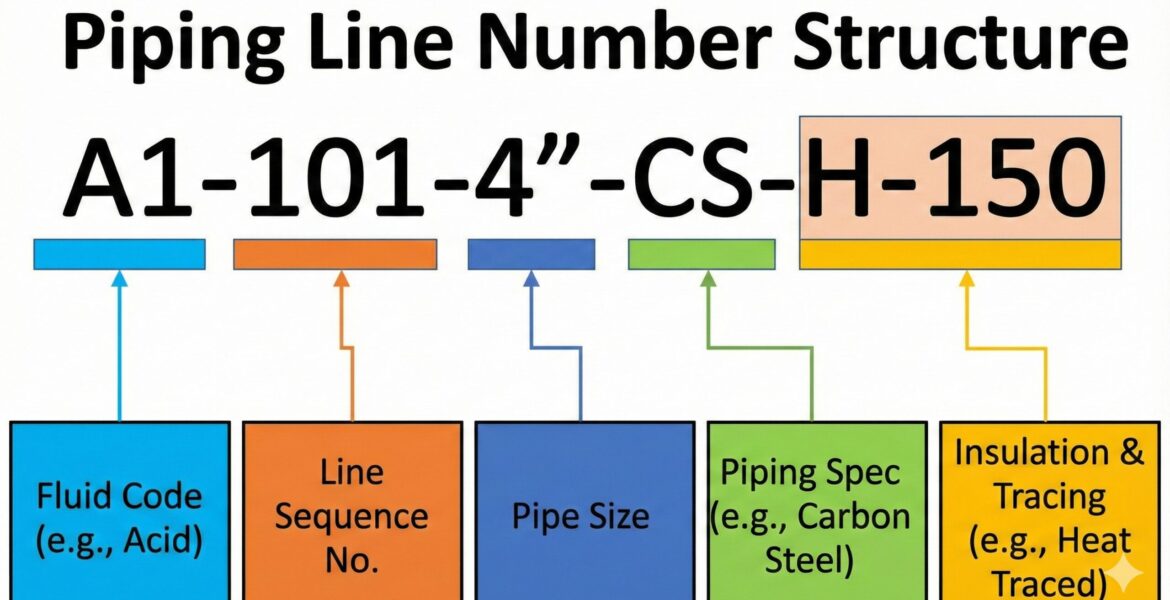
A line number acts as a unique, non-ambiguous identifier for every pipe segment within a facility. It is a condensed code that conveys vital engineering and operational data about the fluid being carried, the piping material specification, and the design conditions. This coding system establishes a universal language that allows various stakeholders—including engineers, designers, fabricators, construction crews, and maintenance personnel—to communicate precisely about the entire network.
The importance of this system can be categorized into several key areas:
1. Safety and Risk Management
In any industrial plant, mixing incompatible fluids or using incorrect piping materials can lead to catastrophic failures. The line number is the primary mechanism for preventing such errors. The unique identifier links the physical pipe to its official engineering documentation, specifically the Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID).
- Hazard Identification: The line number typically contains a code for the fluid service (e.g., ‘W’ for Water, ‘HC’ for Hydrocarbon). This immediate identification is critical for safety personnel responding to leaks or emergencies, guiding them on the necessary precautions and cleanup procedures.
- Material Verification: By linking to a specific material specification class, the line number ensures that the correct pipe grade, wall thickness, and fitting type are used, guaranteeing the piping can withstand the required pressure and temperature limits.
2. Design and Engineering Efficiency
During the design phase, the line number is indispensable for tracking progress and managing technical information.
- P&ID Development: The line number is the cornerstone of the P&ID, forming the basis for process flow, instrumentation hook-ups, and equipment connections.
- Stress Analysis and Support Design: Pipe stress analysts use line numbers to identify critical lines requiring detailed analysis and special support structures. Without consistent numbering, coordinating the outputs of stress analysis with the 3D model would be chaotic.
- Information Management: The line number serves as the primary key in database systems used for materials management (MTO – Material Take-Off) and isometric drawing generation. This systematic organization drastically reduces the time spent searching for information and minimizes data entry errors.
3. Construction and Fabrication
Accurate line numbering translates directly to efficient construction and error reduction on-site.
- Spool Fabrication: Line numbers are stamped or labeled on pipe spools in the fabrication shop. This allows construction crews to identify and install the correct spool piece in the exact design location, avoiding costly rework and schedule delays.
- Testing and Commissioning: The system facilitates the organized pressure testing of piping systems. Testing packages are defined by groups of line numbers, ensuring that all joints and welds are checked against design criteria before the facility becomes operational.
4. Operations and Maintenance
Once a plant is operational, line numbering continues to be critical for daily activities.
| Operational Activity | Role of Line Numbering |
| Troubleshooting | Quick identification of the problematic line and its associated process fluid and design conditions. |
| Isolation and Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) | Clearly defines the exact piping segment that needs to be isolated for maintenance, preventing accidental startup. |
| Documentation Control | Serves as a reference point for accessing the complete history of a pipe segment, including inspection reports and maintenance logs. |
| Inventory Management | Ensures the correct replacement parts are ordered based on the line’s material specification. |
Conclusion
The effective implementation of a standardized line numbering scheme is a hallmark of professional piping design. It provides a foundation of clarity, safety, and efficiency that permeates every stage of a project, from initial concept to final operation. Investing time in developing a clear, robust, and consistent numbering system saves far more in construction costs, prevents operational failures, and ultimately secures the long-term safety and reliability of the industrial asset. All engineering stakeholders must adhere strictly to the established line numbering protocol, treating it as an essential design deliverable rather than a secondary administrative task.