Non-Metallic Piping: Advantages, Applications, and Design Considerations (e.g., FRP, GRE, HDPE) 🚫🔩
0 comments
Non-Metallic Piping: Advantages, Applications, and Design Considerations (e.g., FRP, GRE, HDPE) 🚫🔩
Introduction:
Moving beyond metals. The growing importance and application of non-metallic piping materials in various industries.
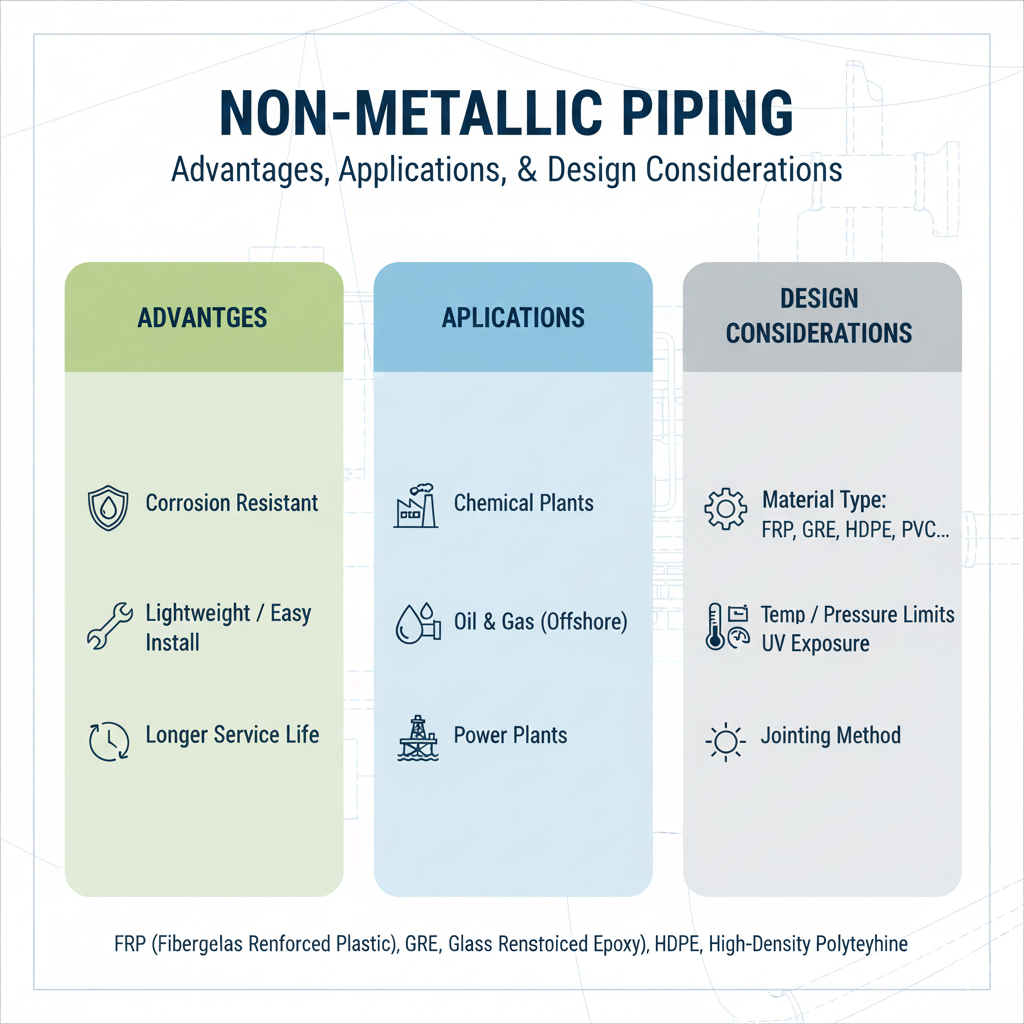
Why Consider Non-Metallic Piping ?
- Excellent Corrosion Resistance: Often superior to metals in aggressive chemical services (acids, caustics, saltwater).
- Light Weight: Easier handling, transportation, installation. Reduced support requirements.
- Lower Installation Costs (potentially): Due to lighter weight and sometimes simpler joining methods.
- Smooth Bore: Reduced friction, lower pumping costs, less prone to scaling or fouling.
- Electrical Non-Conductivity: Important in some applications.
- Good Thermal Insulation Properties (some types).
Common Types of Non-Metallic Piping Materials:
- Thermoplastics: Soften on heating, harden on cooling.
- Polyethylene (PE) / High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE): Water, gas distribution, slurries, chemical waste. Joined by heat fusion. Very ductile.
- Polypropylene (PP): Good chemical resistance, higher temperature rating than PE. Hot water, chemical drainage, industrial applications.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) / Chlorinated PVC (CPVC): Water distribution, drainage, irrigation, some chemical services. CPVC has higher temperature rating. Joined by solvent cement or threads.
- Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF): Excellent chemical and temperature resistance, high purity applications.
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Drain, waste, vent (DWV) applications.
- Thermosets (Reinforced Plastics): Harden permanently after curing. Often composites.
- Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) / Glass Reinforced Epoxy (GRE) / Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP):
- Composition: Glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix (e.g., polyester, vinyl ester, epoxy).
- Properties: High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance.
- Applications: Chemical processing, desalination, power plants (cooling water), oil & gas (produced water, some hydrocarbons).
- Reinforced Thermoset Resin (RTR) Pipe.
- Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) / Glass Reinforced Epoxy (GRE) / Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP):
- Thermoplastics: Soften on heating, harden on cooling.
Key Design Considerations for Non-Metallic Piping (often different from metallic):
- Lower Strength and Stiffness: Requires more supports, shorter spans.
- Higher Thermal Expansion Rate: Flexibility and support design are critical. Expansion loops or joints may be needed more frequently.
- Temperature Limitations: Each material has a specific operating temperature range. Derating of pressure capability at higher temperatures.
- Pressure Rating: Often lower than metallic pipes for a given size. Subject to creep and stress rupture over time.
- Susceptibility to UV Degradation (some types if not protected).
- Impact Resistance: Can be lower than metals, requiring protection in some areas.
- Joining Methods: Solvent cementing, heat fusion, flanging, adhesive bonding, bell-and-spigot with O-rings. Quality of joints is crucial.
- Support Design: Must prevent point loads, often require wider supports or full saddles. Continuous support for some types.
- Abrasion Resistance (varies).
- Fire Resistance (a major concern for some applications/materials).
Relevant Standards for Non-Metallic Piping:
- ASME NM.1 (Thermoplastic Piping Systems), NM.2 (Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Thermosetting-Resin Piping Systems), NM.3 (Nonmetallic Materials). These are relatively new post-construction standards.
- ASME B31.3 Chapter VII (Nonmetallic Piping and Piping Lined With Nonmetals): Provides design, fabrication, and testing rules for non-metallics within its scope.
- ASTM Standards: Many ASTM specs for different types of non-metallic pipes and fittings (e.g., ASTM D2564 for solvent cement for PVC, ASTM F714 for HDPE pipe).
- AWWA Standards: For water applications.
- ISO Standards: (e.g., ISO 14692 for GRP piping in petroleum/natural gas).
Applications and Case Studies:
- Examples of successful non-metallic piping use in different industries.
Conclusion & Call to Action:
- Non-metallic piping offers significant advantages in specific applications, particularly where corrosion is a major issue. However, their design and installation require specialized knowledge due to their unique properties. Courses covering the design, material selection, installation, and relevant codes (like ASME B31.3 Chapter VII and ASME NM standards) for non-metallic piping systems are essential for engineers looking to leverage these materials effectively and safely.
Related Posts
Key Responsibilities of a Piping Engineer 🏗️
December 19, 2025
Future Trends in Piping Engineering
December 14, 2025