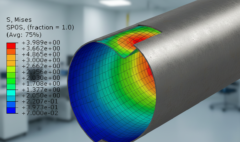
Mastering the Invisible Forces: An Introduction to Piping Stress Analysis Engineering

Mastering the Invisible Forces: An Introduction to Piping Stress Analysis Engineering
Introduction
Piping systems are the lifelines of industrial plants, transporting vital fluids, gases, and slurries across complex networks. While their primary function might seem straightforward, ensuring their structural integrity and operational reliability is a sophisticated discipline: Piping Stress Analysis Engineering. This crucial field focuses on evaluating the stresses, deflections, and forces acting on piping systems to prevent failures, optimize designs, and ensure compliance with safety regulations.
What is Piping Stress Analysis?
At its core, piping stress analysis involves a detailed examination of how various loads impact a piping system. These loads can be static (like gravity, internal pressure, and sustained weight) or dynamic (such as seismic events, wind, and fluid hammer). Engineers use specialized software and analytical methods to predict the behavior of the piping under these conditions. The goal is to ensure that the stresses remain within acceptable limits for the material, preventing issues like fatigue, excessive deformation, and ultimately, catastrophic failures.
Why is it So Important?
The consequences of piping failures can be severe, ranging from production downtime and environmental damage to injuries or even fatalities. Proper stress analysis contributes to:
- Safety: Protecting personnel and the public by preventing leaks, ruptures, and collapses.
- Reliability: Ensuring continuous operation and minimizing unexpected shutdowns.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Optimizing material usage, reducing maintenance needs, and avoiding costly repairs.
- Compliance: Meeting stringent industry codes and standards, which are often legally mandated.
Applicable Codes and Standards
Piping stress analysis is heavily governed by a set of globally recognized codes and standards that provide guidelines for design, fabrication, inspection, and testing. These documents ensure a consistent level of safety and quality across the industry. Some of the most prominent ones include:
- ASME B31 Series: Developed by the ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers), this is perhaps the most widely used set of codes for pressure piping. Different sections cater to various applications:
- ASME B31.1: Power Piping (for electric power generating stations, industrial and institutional plants).
- ASME B31.3: Process Piping (for chemical plants, refineries, petroleum, and natural gas production facilities).
- ASME B31.4: Pipeline Transportation Systems for Liquids and Slurries.
- ASME B31.8: Gas Transmission and Distribution Piping Systems.
- European Standards (EN 13480): For metallic industrial piping, this standard provides comprehensive requirements for design, materials, manufacturing, installation, inspection, and testing.
- Other Relevant Standards: Depending on the specific industry and location, other standards like API (American Petroleum Institute), TEMA (Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association), and local regulations may also apply.
Tools of the Trade: Software for Stress Analysis
Modern piping stress analysis relies heavily on sophisticated software tools that can model complex piping geometries and perform intricate calculations. These programs allow engineers to simulate various loading scenarios and visualize stress distributions. Some of the industry-leading software packages include:
- CAESAR II: A widely recognized and powerful software for pipe stress analysis, capable of handling static and dynamic analyses.
- ROHR2: Another popular and comprehensive pipe stress analysis program, particularly strong in European markets.
- PDMS / E3D: While primarily 3D plant design software, PDMS and its successor E3D (AVEVA E3D Design) can integrate with stress analysis tools or have modules that assist in preparing models for analysis.
- Smart 3D: Intergraph Smart 3D (part of Hexagon’s offerings) is a data-centric, rule-driven design solution that often works in conjunction with stress analysis software by providing accurate geometric and material data.
Conclusion
Piping stress analysis engineering is an indispensable discipline that underpins the safety and efficiency of industrial operations worldwide. By understanding the forces at play and adhering to rigorous codes and standards, engineers ensure that piping systems operate reliably, protecting both assets and lives. The continued evolution of specialized software further empowers these professionals, allowing for more accurate and efficient analysis in an ever-complex industrial landscape.