The U-Bolt: Deceptively Simple
Pipe Supports
1. Definition & Function Deep Dive
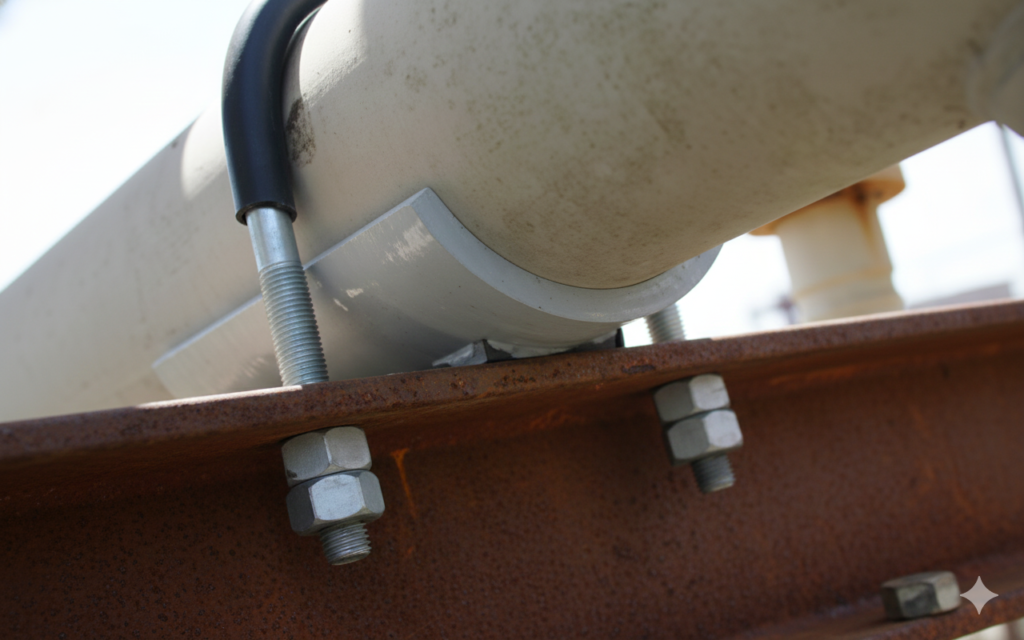
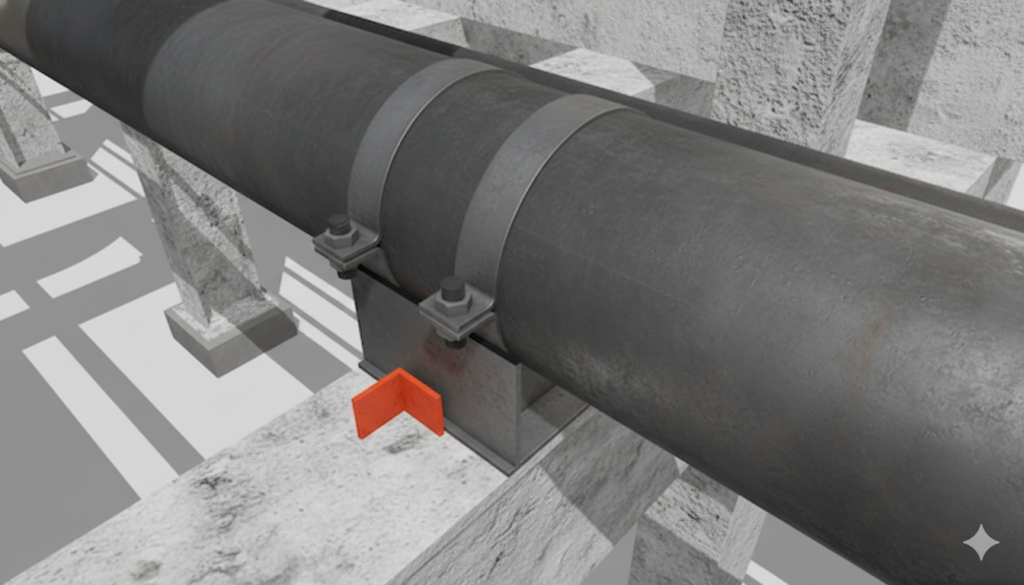
It looks like a piece of hardware store kit, but in industrial piping, the U-Bolt requires respect. It is primarily a guide—it holds the pipe down onto a support but allows it to slide axially.
2. Codes & Application
Used extensively in smaller bore utility piping (water, air). MSS SP-58 Type 24.
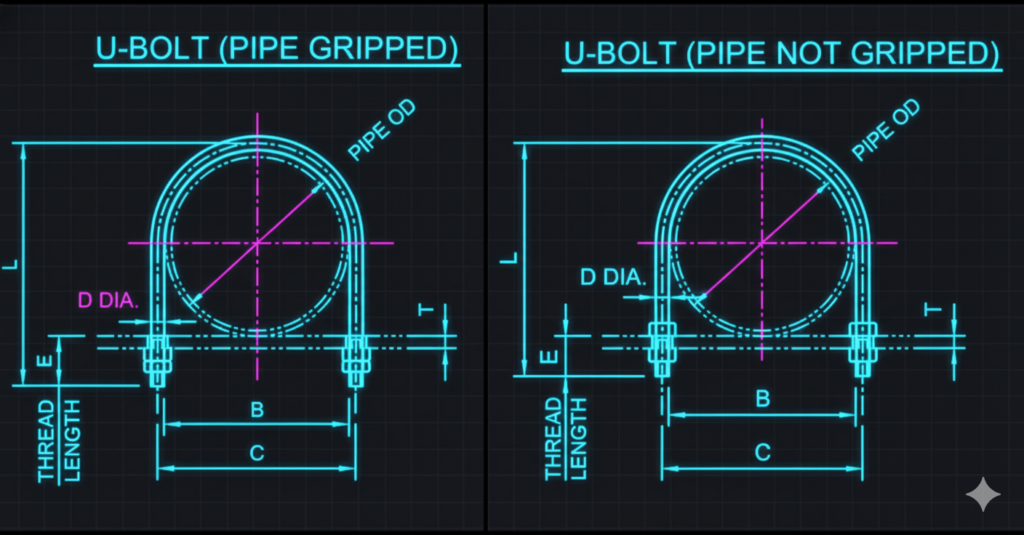
3. The Critical “Grip” vs. “Non-Grip” Distinction
- Non-Grip (Guide): In 90% of applications, the U-bolt should not be tightened snugly against the pipe. There should be a small gap (often 1/16″) between the crown of the U-bolt and the top of the pipe. This allows the pipe to slide.
- Grip (Anchor/Stop): Sometimes, on small lines, a U-bolt is used to stop movement entirely. This requires torquing the nuts down to create friction. This must only be done if explicitly called for by the design engineer.
4. Troubleshooting & Accidents
- The Pipe Crusher: A common mistake by inexperienced installers is treating a U-bolt like a muffler clamp, impact-wrenching the nuts until the pipe ovalizes. This damages thin-wall stainless piping and prevents axial thermal movement, leading to massive stress buildup elsewhere.
- The Loosening Nut: Because pipes vibrate, U-bolt nuts tend to back off over time. Critical applications require “double-nutting” to lock them in place.